Configuring PyCharm
Overview
If you use PyCharm for developing there are a few things you need to configure in order to be able to run and debug.
This document describes a few useful configurations for sentry development
Configurations:
Python interpreter: (make sure it is the venv interpreter) e.g. ~/venv/sentry/bin/python
To create a configuration (a run/debug configuration) just go to Run | Edit Configurations... (also available in the default toolbar).

Test runner
Sentry uses pytest for its unit tests.
Create a pytest configuration (under Python tests)
Set Target: Custom
Additional Arguments: tests/sentry
Dev server with everything needed
For running (not debugging) with everything set up (web, workers, cron):
- Create another Python configuration
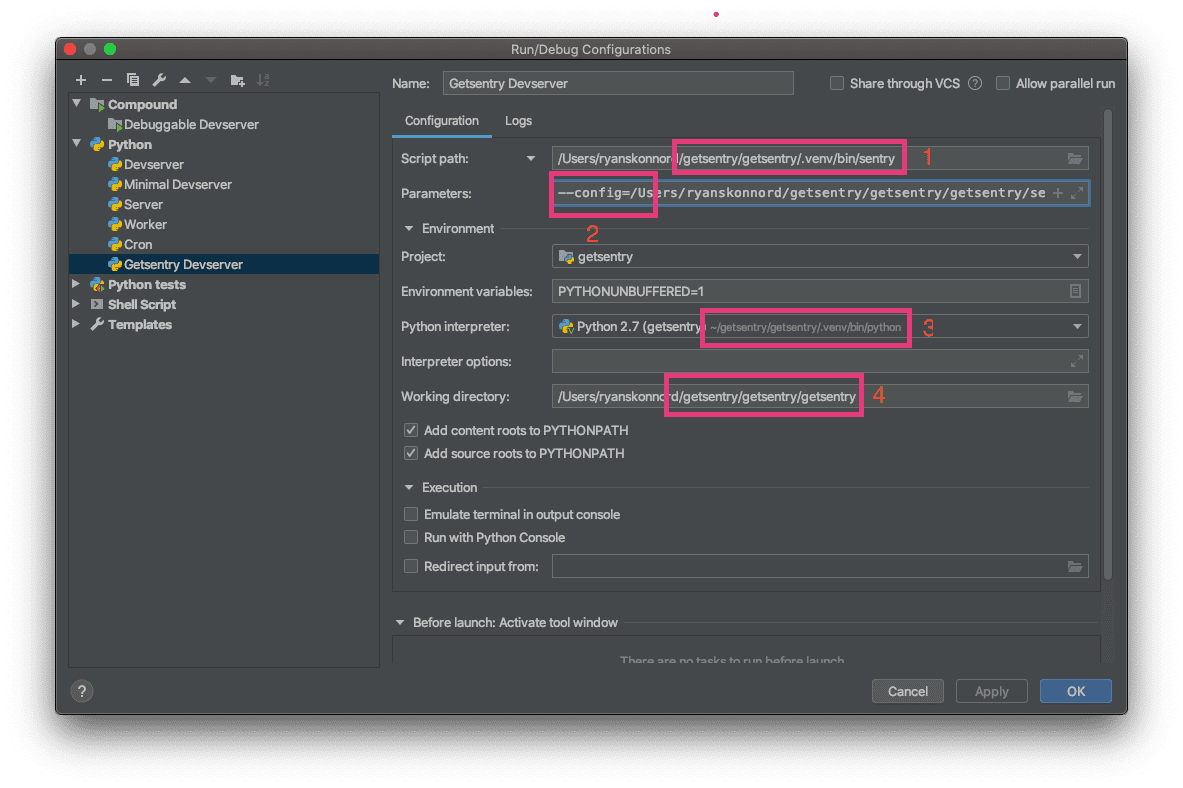
- Script path:
<venv dir>/bin/sentrye.g.~/venv/sentry/bin/sentry - Parameters:
devserver --workers - Python interpreter: the venv interpreter
- Working dir: (the
srcpath in your sentry installation directory ) e.g. ~/dev/sentry/src
Note: You will not be able to debug the web workers with this configuration (the web worker is started by invoking a uwsgi server and I couldn't find a way to attach to it).

Getsentry dev server with everything needed
You can duplicate a Sentry devserver run configuration to run from the "getsentry" repo, with the following changes:
- Change the script path to
getsentry/.venv/bin/sentrywithin your getsentry project. (Not to be confused with.venv/bin/getsentry, which is a bash script.) - Prepend the parameters with
--config=<your path>/getsentry/getsentry/settings.py. So the full value should look like--config=.../settings.py devserver --workers. - Change the Python interpreter to point at
.venv/bin/pythonwithin your getsentry project. You may need to go into PyCharm's global "Preferences" window and add it as a project interpreter ("Project: sentry > Project Interpreter"). - Change the working directory to
getsentry/getsentry.
Note that the paths in step 2 and 4 refer to the directory named getsentry within the repository named getsentry. If the repository also has a parent directory named getsentry to correspond to the GitHub org name, the correct paths may contain getsentry/getsentry/getsentry.
Debugging with PyCharm
The devserver command exists mainly to spawn daemons in separate processes, which means it is not very useful to attach a debugger to it in its default mode.
Web server
The devserver command has a special flag that will cause the web server to be launched in a thread of the same process (rather than as the web daemon). This allows the same PyCharm "Debug" action that launches the devserver to attach to the web server and hit breakpoints on its back end.
Clone your devserver run configuration and add --debug-server to the end of the "Parameters" field. Launch it by selecting "Debug" rather than "Run".
The --debug-server flag may cause the process to not respond correctly to SIGINT and to shut down less gracefully than your original configuration. It is recommended to keep both, using the first with the "Run" command and the second with the "Debug" command.
You may keep the --workers flag alongside --debug-server, but note that it will not be possible to attach breakpoints to the workers, nor to any other daemons spawned by the devserver.
Stand-alone daemons
To attach a debugger to an individual daemon other than web, create a run configuration for the daemon. The following attributes should be the same as your devserver config. (You may clone it and change only the "Parameters" field.)
- Script path:
<venv dir>/bin/sentrye.g.~/venv/sentry/bin/sentry - Python interpreter: the venv interpreter
- Working dir: (the
srcpath in your sentry installation directory ) e.g.~/dev/sentry/src
Set the new run configuration's parameters to a run command that launches the daemon, such as:
run cronrun worker -c 1
Tips and troubleshooting
- The same set of modifications will work on run configs for the
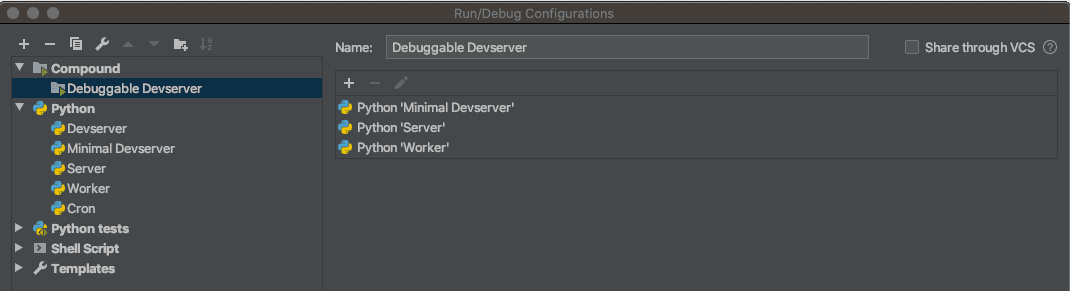
getsentryproject, if you want to debug that. - PyCharm's "Compound" run configuration type is useful for launching several run configurations at once. It may be convenient to set one up if you are debugging one or more stand-alone daemons in concert with a devserver.
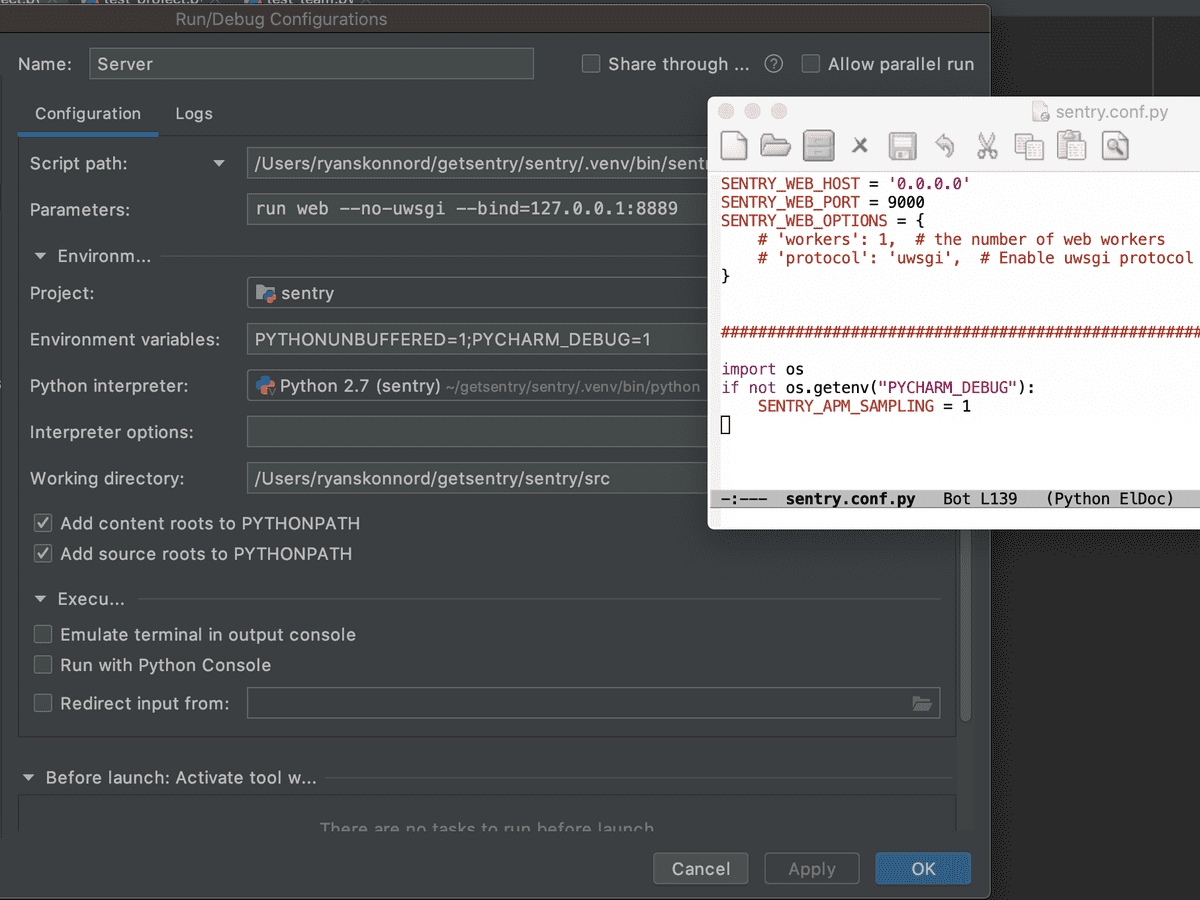
- If you would like Sentry to behave differently in a debugging environment than in a regular run, you can add arbitrary environment variables and then check for them in your
.sentry/sentry.conf.pyfile. For example, the screenshot below shows a setup where APM sampling is disabled while debugging (since stopping on breakpoints would pollute time measurements). Note thatPYCHARM_DEBUGis an arbitrary name; it has no special meaning to PyCharm nor to Sentry.
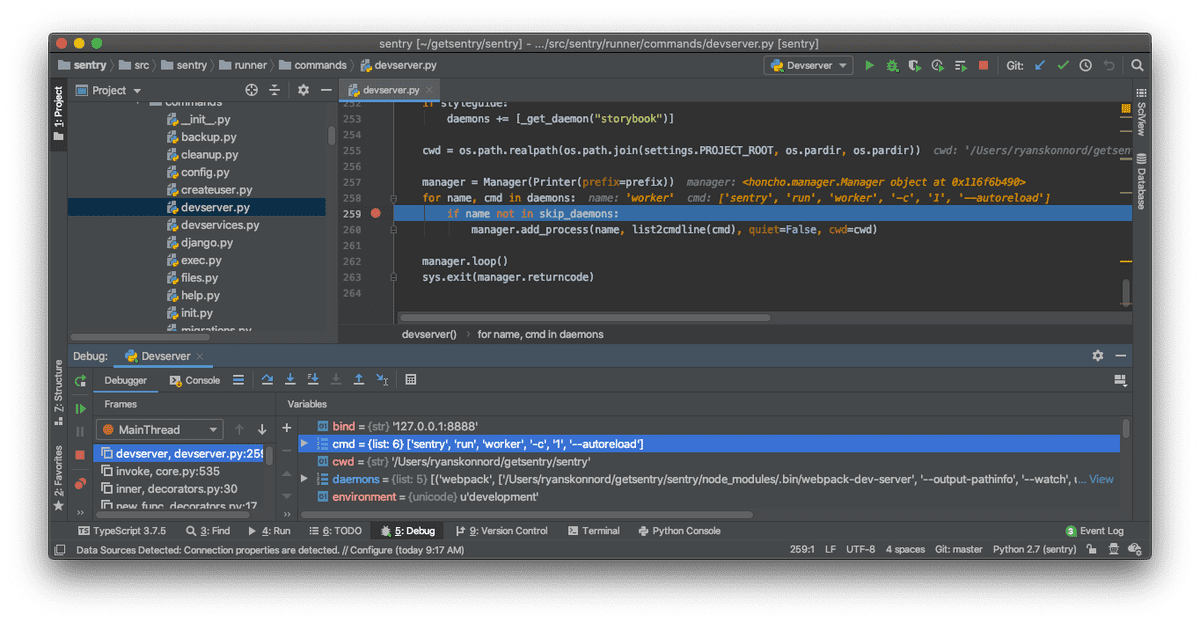
- If your individually-run daemons are not working, you can troubleshoot by debugging
devserver --debug-serverand inserting breakpoints onsrc/sentry/runner/commands/devserver.py. This will let you manually inspect the commands that thedevservercommand is running. (Look for themanager.add_processcall near the bottom.) Try adjusting the parameters in your run configs to match those commands if they don't already.